Creating a Function in MATLAB
Functions in MATLAB can be
interpreted as programs. The function consists of one or several commands in
MATLAB. The MATLAB function is stored in m-files. M-files are text files
containing MATLAB commands and stored with the .m extension. Editors to create m-files
can be activated using the toolbar. The function has a special syntax on the
first line. In general the syntax is:
function [out1, ..., outM] =
func_name (in1, ..., inN)
A function does not have to be
written with an input or output argument (out1, ..., OutM is the output
argument, while in1, ..., inN is the input argument). The functions written
above will be stored in a file with the name func_name.m. The function has its
own workspace. Information communication between the workspace function and the
main workspace is done through input and output variables. It's a good idea to
put a few lines of comments at the beginning of a function to explain the
usefulness of the program.
The following will be given
three simple m-file examples using the input and output arguments. The three
files are:
Example 1. Addition of Two Variables (scalar / vector / matrix)
To
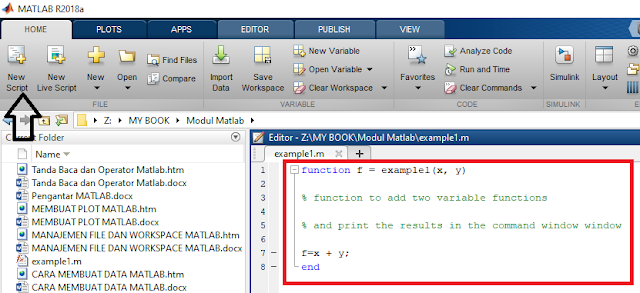
create a new function in MATLAB, the first step to do is to add New Script.
where the procedure for writing the correct addition function is as below,
function f = example1(x,
y)
% function to add two
variable functions
% and print the results in
the command window
f=x + y;
end
After that save it with the
file name is example1.m
To
call a function that was created before, open the folder location where
Example1.m is stored. After that, call it by writing the name of the function
in the Command Window as below,
Example 2 Summing three variables (scalar / vector / matrix).
Like
example 1, create a new script with the name of the function example2 and save
it in the same folder as the function example1. Where the example2 function has
three input arguments (x, y, and z) and one output argument (s).
function
s=example2(x,y,z)
% Adds three variables
% and save the results
s=x+y+z;
end
Now call the function that has
been created as shown in the image below,
Example 3 Calculate the number
and multiplication of two variables (scalar / vector / matrix)
Below is an m-file with the
name function example3. Two input arguments (x and y) and two output arguments
(s and p). M-file to calculate the number and multiplication of two variables
then save the results (save with file name A: \ example3.m).
function [s, p] =
example3 (x, y)
% calculates the number and
multiplication of two variables
% and save the results
s = x + y;
p = x * y;
end
The function in Example3 can
be called in the following way,
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER



This is also a very good post which I really enjoyed reading. It is not every day that I have the possibility to see something like this.. PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE
ReplyDelete